The concept of intelligence ownership has been gaining traction in recent years, and for good reason. As Cisco has demonstrated, owning intelligence rather than renting it can be a game-changer for enterprises looking to scale their operations securely. According to a recent article by The Rundown AI, Cisco’s strategy to scale agents securely and reshape enterprise workflows is a prime example of this shift.
The Importance of Intelligence Ownership
Owning intelligence means having control over the data, algorithms, and insights that drive business decisions. This is particularly crucial in today’s fast-paced, data-driven world, where artificial intelligence and machine learning are becoming increasingly prevalent. By owning their intelligence, enterprises can ensure that their systems are secure, transparent, and aligned with their overall goals.
Scaling Agents Securely with Cisco

Cisco’s approach to scaling agents securely is centered around the idea of intelligence ownership. By developing and owning their own AI-powered agents, Cisco is able to ensure that their systems are secure, efficient, and tailored to their specific needs. This approach has allowed Cisco to reshape their enterprise workflows and improve overall productivity. As AWS and other cloud providers continue to evolve, the importance of owning intelligence will only continue to grow.
Cisco’s strategy is a great example of how owning intelligence can help enterprises scale their operations securely and efficiently. By taking control of their data and algorithms, companies can ensure that their systems are aligned with their overall goals and values.
The Benefits of Owning Intelligence
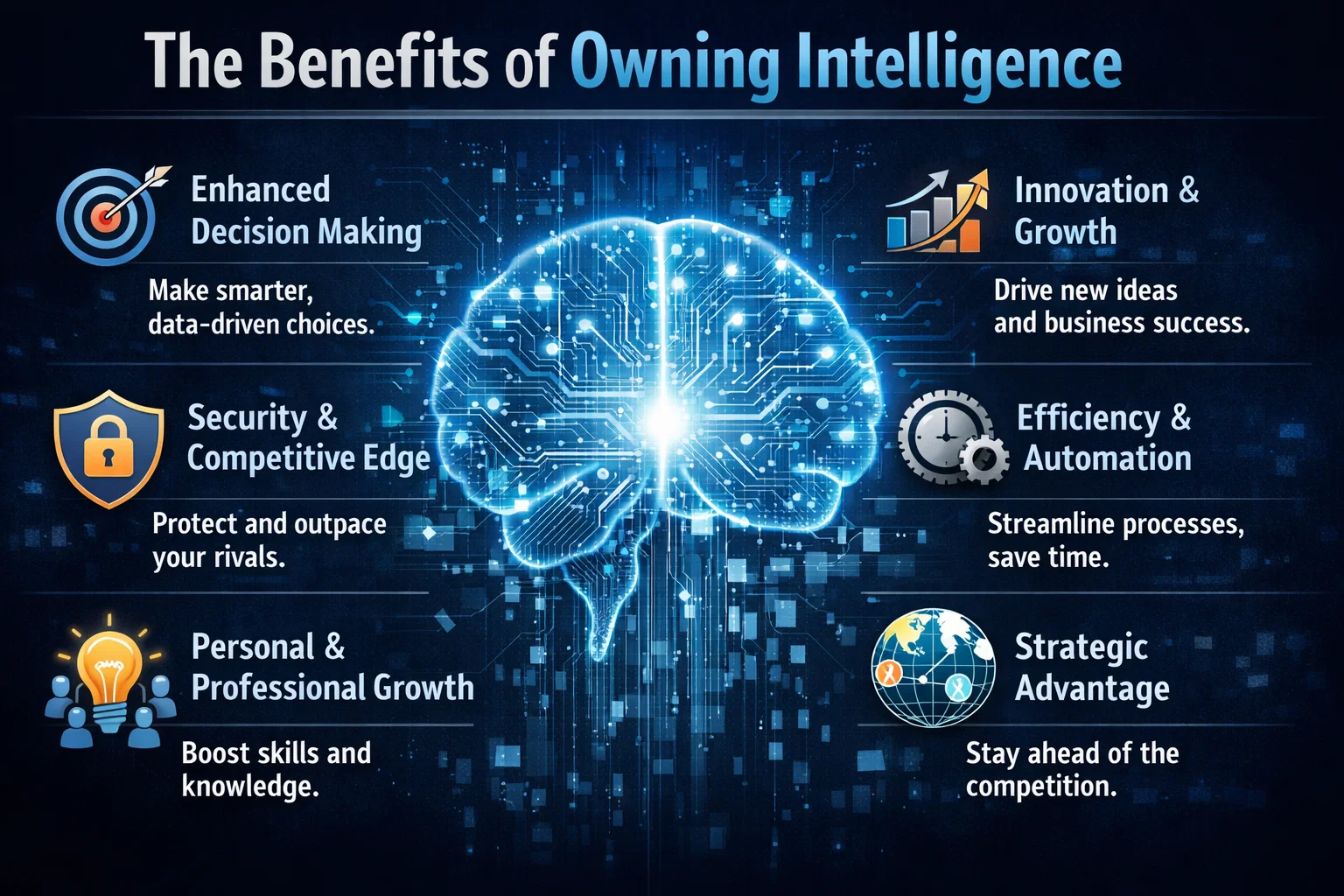
So why should enterprises prioritize intelligence ownership? The benefits are numerous. For one, owning intelligence provides a level of control and transparency that is difficult to achieve with rented intelligence. It also allows enterprises to develop systems that are tailored to their specific needs and goals, rather than relying on generic, off-the-shelf solutions. Additionally, owning intelligence can help enterprises to improve their overall security posture, as they are able to develop and implement their own security protocols and measures.
In contrast, rented intelligence can be limiting and inflexible. When enterprises rely on rented intelligence, they are often at the mercy of the provider, with limited control over the data, algorithms, and insights that drive their business decisions. This can lead to a lack of transparency, security risks, and a general sense of disempowerment.
Real-World Applications
So what does intelligence ownership look like in practice? One example is the development of custom GitHub repositories, which allow enterprises to own and control their code and data. Another example is the use of Azure and other cloud platforms to develop and deploy custom AI-powered solutions. By taking control of their intelligence, enterprises can develop systems that are tailored to their specific needs and goals, and that provide a level of security, transparency, and efficiency that is difficult to achieve with rented intelligence.