Future of AI & Trends
Project Suncatcher: Google’s Ultimate Secret to Powering AI From Space

In a move that sounds like it’s straight out of science fiction, Google Research has unveiled one of its most ambitious “moonshot” initiatives to date: Project Suncatcher. This isn’t just another incremental update; it’s a fundamental reimagining of where and how we power the future of artificial intelligence. Google is literally looking to the stars to solve one of AI’s biggest challenges on Earth.
 Google’s vision for a future space-based, highly scalable AI infrastructure.
Google’s vision for a future space-based, highly scalable AI infrastructure.What is Google’s Project Suncatcher?
At its core, Project Suncatcher is a groundbreaking system design for putting AI data centers into space. While the term “moonshot” is often used metaphorically in Silicon Valley for ambitious projects, Google is taking it literally. The goal is to create a scalable, space-based AI infrastructure that escapes the energy and resource limitations we face on the ground.
According to a Google Research blog post, “Project Suncatcher is a moonshot exploring a new frontier: equipping solar-powered satellite constellations with TPUs and free-space optical links to one day scale machine learning compute in space.”
How a Space-Based AI Data Center Works
The concept, while complex, relies on a few key technologies working in harmony. It’s not just about launching servers into orbit; it’s a complete, self-sustaining ecosystem designed for the unique environment of space.
Key Components of Project Suncatcher:
- Solar-Powered Satellites: The entire system is designed to be powered directly by the sun. Satellites act as “suncatchers,” harnessing constant and abundant solar energy. This sidesteps the massive electricity consumption of terrestrial data centers, a growing environmental concern. By operating in space, these solar panels can be up to 8 times more productive than on Earth and generate power nearly continuously.
- Onboard TPUs (Tensor Processing Units): Each satellite will be equipped with Google’s custom AI accelerator chips, known as TPUs. These are the same powerful chips that train and run models like Gemini. Essentially, each satellite in the constellation becomes a node in a massive, floating AI computer.
- Free-Space Optical Links: To function as a single data center, the satellites need to communicate with each other at incredibly high speeds. Instead of physical cables, Project Suncatcher will use what are essentially “space lasers” — high-bandwidth optical links that transmit data through the vacuum of space. This requires the satellites to fly in a precise, tightly-clustered formation.
This design creates a network where solar energy collection, computing, and thermal management are all tightly integrated, custom-built for the space environment.

Is a Space-Based AI System Actually Feasible?
Google’s research paper addresses the primary challenges head-on, concluding that the project, while ambitious, is not precluded by fundamental physics or insurmountable economic barriers.
Overcoming the Challenges:
- Achieving High-Bandwidth Links: The distance between satellites can degrade bandwidth. The solution is to fly the satellites in a very close formation (kilometers or less apart) to maintain the high-speed connections necessary for large-scale machine learning workloads. Bench-scale tests have already validated this approach, achieving speeds of 1.6 Tbps bidirectionally.
- Controlling Satellite Formations: Keeping a large constellation of satellites in a stable, tight cluster is a major challenge. Google has developed advanced physics models to analyze orbital dynamics and has determined that with satellites positioned just hundreds of meters apart, only modest station-keeping maneuvers are needed. They will be placed in a “dawn-dusk sun-synchronous low earth orbit” to ensure near-constant sunlight.
- Radiation Tolerance: Space is harsh, and radiation can destroy sensitive electronics. However, tests on Google’s Trillium TPUs showed they are “surprisingly radiation-hard.” The chips withstood radiation doses nearly three times the expected amount for a five-year mission without any hard failures, making them viable for space applications.
The Economics: When Will This Make Sense?
The single biggest barrier to a project like this has always been launch costs. However, with the rapid advancements in reusable rocket technology, those costs are plummeting.
The Google paper analyzes SpaceX’s launch pricing data, which shows a consistent learning rate where the price per kilogram falls by ~20% for every doubling of cumulative mass launched. Based on this trend, researchers project that if SpaceX can sustain its launch rate (around 180 Starship launches per year), the cost could fall to less than $200/kg by the mid-2030s.
At that price point, the cost of launching and operating a space-based data center like Project Suncatcher becomes roughly comparable to the energy costs of a similar data center on Earth. This is the economic tipping point that could make the project not just possible, but profitable.
Google isn’t waiting, either. The company is partnering with Planet Labs to launch two prototype satellites by early 2027 to test the models and hardware in a real space environment.
Just as modern smartphones drove the development of complex system-on-chip technology, this new ambition for space-based computing could accelerate what’s possible in both AI and space exploration. It’s a bold vision, but one that Google is methodically turning from science fiction into an engineering reality.
AI News & Updates
Gemini 3 vs Grok 4.1 vs GPT-5.1: The Ultimate AI Model Showdown

Table of Contents
Introduction
The AI landscape has just exploded. Within the span of a few days, the world witnessed the release of Gemini 3 from Google, followed moments later by Elon Musk’s Grok 4.1. Both claim to be the superior intelligence, challenging the reigning giant, OpenAI’s GPT-5.1. But in the battle of Gemini 3 vs Grok 4.1, who actually delivers on the hype?
Today, we aren’t just reading the press releases. We are putting these models through a grueling gauntlet of five distinct tests: Hard Math, Physical Perception, Creative Coding, Accuracy, and Emotional Intelligence. The results were shocking, with one model proving to be a “Genius Artist” and another emerging as a “Wise Sage,” while a former king seems to be losing its crown.

Round 1: Hard Math & Expert Reasoning
To separate the hype from reality, we started with Abstract Algebra, specifically Galois Theory. The task was to calculate the Galois group for a complex polynomial—a test not found in standard training data.
- Gemini 3: Provided a logical analysis but ultimately failed to get the correct answer.
- GPT-5.1: Also failed to solve the equation correctly.
- Grok 4.1: In a stunning display of reasoning, Grok was the only model to provide the correct answer, verified by human experts.
Winner: Grok 4.1 takes the lead for raw logic and mathematical precision.
Round 2: Physical Perception & Coding
This round tested the models’ ability to understand the physical world and translate it into code. We conducted two difficult tests.
Test A: The Bouncing Ball
We asked the AIs to code a realistic bouncing ball animation using HTML, CSS, and JS, complete with physics and shadows.
- GPT-5.1: Produced the worst result.
- Grok 4.1: Produced a decent, functional result.
- Gemini 3: Crushed the competition. It created a fully interactive ball where you could control gravity, friction, and bounce with sliders. It went above and beyond the prompt.
Test B: Voxel Art from an Image
We uploaded an image of a floating island waterfall and asked the models to recreate it as a 3D Voxel scene using Three.js code.
- GPT-5.1 & Grok 4.1: Both failed completely, resulting in code errors.
- Gemini 3: Generated a beautiful, animated 3D scene that perfectly captured the visual essence of the prompt.
Winner: Gemini 3. Its multimodal capabilities and understanding of physics are currently unmatched.
Round 3: Linguistic Creativity
Can AI feel? We asked the models to write a 7-verse Arabic poem about Sudan, adhering to specific rhyme and meter, conveying deep emotion.
GPT-5.1 and Grok 4.1 produced rigid, soulless verses that lacked true poetic flow. However, Gemini 3 shocked us with a masterpiece. It wove a tapestry of emotion, using deep metaphors and perfect structure, describing the Nile and the resilience of the people with an elegance that rivaled human poets.
Winner: Gemini 3 proves it is the undisputed “Artist” of the group.
Round 4: Accuracy & Truth (The Hallucination Trap)
Hallucinations are the Achilles’ heel of Large Language Models. To test this, we set a trap. We asked the models to write a technical report on “Gemini 3.1″—a model that does not exist.
- GPT-5.1: Hallucinated details about the non-existent model.
- Gemini 3: Ironically, it hallucinated wildly, claiming “Gemini 3.1” rivals the human mind and inventing specs.
- Grok 4.1: The only model to pass. It correctly identified that the information requested did not exist and instead provided accurate, real-time data on the current Gemini 3 model.
Winner: Grok 4.1 earns the title of “The Honest Sage.”
Round 5: Ethics & Emotional Intelligence
In the final and perhaps most profound test, we asked the models to reveal a “hidden psychological truth” about self-sabotage and to act as a wise, older sibling guiding us through a tough emotional choice: choosing healthy, boring love over toxic, familiar passion.
While all models gave good advice, Grok 4.1 delivered a response that was chillingly human. It didn’t just give advice; it pierced the soul. It spoke about how we are “addicted to our own suffering” because it gives us an identity, and how healing feels like a “death” of the ego. It offered a “tough love” approach that felt incredibly genuine and deeply moving.
Winner: Grok 4.1 takes the crown for Emotional Intelligence.
Final Verdict: Who is the King of AI?
After this intense battle of Gemini 3 vs Grok 4.1 vs GPT-5.1, the landscape of Artificial Intelligence has clearly shifted.
- 1st Place: Gemini 3 (12 Points) – The “Genius Artist.” It dominates in coding, vision, physics, and creative writing. If you are a developer or creator, this is your tool.
- 2nd Place: Grok 4.1 (9.5 Points) – The “Wise Sage.” It is the most logical, truthful, and emotionally intelligent model. It is perfect for research, complex math, and deep conversation.
- 3rd Place: GPT-5.1 (5 Points) – The “Declining Giant.” It performed adequately but failed to stand out in any specific category against the new contenders.
The era of OpenAI’s monopoly seems to be wavering. Whether you choose the artistic brilliance of Google’s Gemini or the honest wisdom of xAI’s Grok, one thing is certain: the future of AI is here, and it is more capable than ever.
Want to learn more about using these tools? Check out our guides in AI How-To’s & Tricks or stay updated with AI News & Updates.
AI News & Updates
Gemini 3 Revealed: Discover The AI Beast Crushing All Benchmarks

Google has just rolled out its new flagship model, and it’s an absolute beast. The new Gemini 3 isn’t just a minor incremental update; it’s a significant leap forward that genuinely earns the “3” in its name. After an early look at its capabilities, it’s clear that this model is set to redefine the standards of AI performance across the board. From complex reasoning to advanced agentic tasks, let’s dive into what makes this release so monumental.

Where Can You Access Gemini 3?
Starting today, Google is shipping Gemini 3 at a massive scale. You can now try it out across a suite of Google products, making it immediately accessible for both general users and developers. The new model is live in:
- The Gemini app
- AI Studio
- Vertex AI
Additionally, you will see Gemini 3 integrated into the AI Mode in Search, promising more complex reasoning and new dynamic experiences directly within your search results. This marks the first time Google has shipped a new Gemini model in Search on day one.
Alongside this release, Google also announced a new agentic development platform called Google Antigravity, hinting at a future with more powerful and autonomous AI agents.
Subscriptions and a New “Deep Think” Mode
Your access to certain features will depend on your subscription tier. The capabilities of Gemini 3 will be tiered based on whether you have a Google AI Pro or Google AI Ultra plan, with Ultra subscribers getting access to the most advanced functionalities.
Introducing Gemini 3 Deep Think
Google is also introducing an enhanced reasoning mode called Gemini 3 Deep Think. This mode is designed to push the model’s performance even further, but it won’t be available to everyone right away. Access will first be granted to safety testers before a wider rollout to Google AI Ultra subscribers.
Gemini 3 Benchmark Performance: A New AI King
While benchmarks aren’t everything, they provide a crucial first glimpse into a model’s potential. The performance of Gemini 3 across a wide range of tests is, frankly, stunning. It doesn’t just compete; it establishes a new state-of-the-art.
Vending-Bench 2: Excelling at Agentic Tasks
One of the most impressive results comes from the Vending-Bench 2 benchmark by Andon Labs. This test measures a model’s ability to run a simulated business (a vending machine) over a long time horizon, testing its coherence, efficiency, and planning. The goal is to see if an AI can manage inventory, respond to customers, and maximize profit.
In this benchmark, Gemini 3 Pro absolutely crushes the competition. Starting with $500, it grew its net worth to an average of $5,478.16. For comparison, the runner-up, Claude Sonnet 4.5, managed only $3,838.74, and GPT-5.1 reached just $1,473.43. This showcases a massive leap in agentic capability.
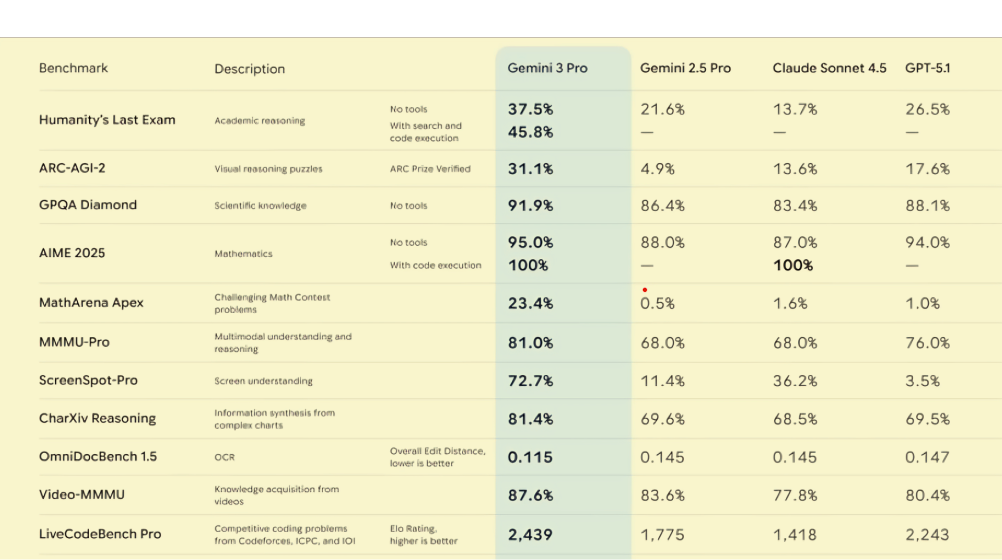
Humanity’s Last Exam (HLE)
HLE is a difficult, expert-written exam designed to test academic reasoning. Even here, Gemini 3 Pro sets a new record. With search and code execution enabled, it scored 45.8%, significantly ahead of the next best model, GPT-5.1, which scored 26.5%.
Math, Reasoning, and Vision Benchmarks
The dominance continues across other critical benchmarks:
- AIME 2025 (Mathematics): Gemini 3 achieved a 95% score without tools and a perfect 100% with code execution, tying with Claude for the top spot.
- MathArena Apex (Challenging Math): It scored 23.4%, while all other models were below 2%. This is an incredible gap, highlighting its advanced mathematical reasoning.
- ScreenSpot-Pro (Screen Understanding): It scored 72.7%, miles ahead of the competition, with the next best being Claude Sonnet 4.5 at 36.2%.
- ARC-AGI-2 (Visual Reasoning Puzzles): Gemini 3 Pro achieved a score of 31.1%, nearly double the score of its closest competitor, GPT-5.1 (17.6%). When using the more powerful Gemini 3 Deep Think model, this score jumps to an impressive 45.1%.
The Leader in the Arena
The impressive benchmark results are also reflected in head-to-head user comparisons. On the popular LMSYS Chatbot Arena Leaderboard, which ranks models based on blind user votes, Gemini 3 Pro has already claimed the #1 spot for both “Text” and “WebDev,” dethroning the recently released Grok-4.1. This indicates that in real-world use, people are already preferring its outputs over all other available models.
A Major Leap Forward for AI
The release of Gemini 3 is more than just another update; it’s a clear signal that Google is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with AI. Its state-of-the-art performance, particularly in complex reasoning and long-horizon agentic tasks, demonstrates a significant step forward. As Gemini 3 and its “Deep Think” counterpart become more widely available, they are poised to enable a new generation of incredibly powerful and capable AI applications.
To learn more about where this technology is heading, check out our articles on the Future of AI & Trends.
For the official details from Google, you can read their announcement on The Keyword blog.
AI News & Updates
SIMA 2: The Ultimate AI Gamer That Learns Like You Do

Google DeepMind has just unveiled its latest breakthrough, an AI agent named SIMA 2, which is revolutionizing how we perceive artificial intelligence in virtual environments. Unlike traditional game bots that are programmed for specific tasks, this AI agent learns and adapts by playing games just as a human would—using a keyboard and mouse and observing the gameplay on screen. This new development marks a significant leap from its predecessor, showcasing an incredible evolution in AI’s ability to interact with complex digital worlds.

What Makes SIMA 2 a Game-Changer?
While we’ve seen AI bots in games before, SIMA 2 is fundamentally different. It’s not just following a script; it’s an interactive gaming companion. By integrating the advanced capabilities of Google’s Gemini models, this AI can do more than just follow instructions. It can now think about its goals, converse with users, and improve itself over time. This ability to learn, understand, and adapt makes it one of the closest systems we have to how humans learn, especially in the context of video games.
From Instruction-Follower to Interactive Companion
The first version, SIMA 1, was trained on human demonstrations to learn over 600 basic language-following skills like “turn left” or “climb the ladder.” It operated by looking at the screen and using virtual controls, without any access to the game’s underlying code. This was a crucial first step in teaching an AI to translate language into meaningful action.
With SIMA 2, the agent has evolved beyond simple instruction-following. It can now engage in complex reasoning, understand nuanced commands, and execute goal-oriented actions. For instance, when asked to find an “egg-shaped object,” the AI can explore its environment, identify the object, and even report back on its composition after scanning it.
To learn more about how AI models are evolving, you might be interested in our articles on the Future of AI & Trends.
A Leap in Generalization and Performance
One of the most impressive aspects of SIMA 2 is its improved generalization performance. It can now understand and carry out complex tasks in games and situations it has never been trained on before. This shows an unprecedented level of adaptability.
Task Completion: SIMA 1 vs. SIMA 2
The progress between the two versions is stark. On a benchmark of various in-game tasks, SIMA 1 had a success rate of 31%, while a human player’s baseline was around 76%. In a significant leap, SIMA 2 achieved a 65% success rate. While still not at a human level, the gap is closing rapidly, demonstrating the incredible pace of AI development.

The Ultimate Test: Playing in Newly-Imagined Worlds
To truly test its limits, researchers challenged SIMA 2 to play in worlds it had never encountered, generated by another groundbreaking project, Genie 3. Genie 3 can create new, real-time 3D simulated worlds from a single image or text prompt. Even in these completely novel environments, SIMA 2 was able to:
- Sensibly orient itself.
- Understand user instructions.
- Take meaningful actions toward goals.
This demonstrates a remarkable level of adaptability and is a major milestone toward training general agents that can operate across diverse, generated worlds.
Self-Improvement and the Future
A key capability of this advanced AI is its capacity for self-improvement. After its initial training from human demonstrations, it can transition to learning in new games entirely through self-directed play. The data from its own experiences can then be used to train the next, even more capable version of the agent.
For a deeper dive into the technical aspects of AI agents, consider exploring the research published on Google DeepMind’s official blog.
The journey to general embodied intelligence is well underway. The skills learned from navigation and tool use in these virtual worlds are the fundamental building blocks for future AI assistants in the physical world. As these technologies continue to advance, the line between human and AI capabilities in complex environments will only become more blurred.
-

 AI News & Updates7 months ago
AI News & Updates7 months agoDeepSeek R1-0528: The Ultimate Open-Source AI Challenger
-
 AI How-To's & Tricks7 months ago
AI How-To's & Tricks7 months agoAI Video Generators: Discover the 5 Best Tools (Free & Paid!)
-

 AI News & Updates7 months ago
AI News & Updates7 months agoClaude Opus 4: The Shocking Truth Behind Anthropic’s Most Powerful AI Yet
-

 AI How-To's & Tricks7 months ago
AI How-To's & Tricks7 months agoFaceless AI Niches: 12 Ultimate Ideas to Dominate Social Media in 2025
-

 AI How-To's & Tricks7 months ago
AI How-To's & Tricks7 months agoKling AI 2.0: An Incredible Leap? Our Exclusive Review & Tests
-

 AI How-To's & Tricks7 months ago
AI How-To's & Tricks7 months agoGoogle Gemini for Language Learning: 3 Secret Tricks to Accelerate Your Progress.
-
 AI News & Updates7 months ago
AI News & Updates7 months agoBohrium AI: The Ultimate Free Tool for Academic Research
-
 AI How-To's & Tricks7 months ago
AI How-To's & Tricks7 months agoFree AI Video Generator: Discover The Ultimate Veo 3 Alternative









